1. INTRODUCTION
Over the years, many sectors have transitioned to the use of ecological materials from synthetic materials including structural applications, whereas the usage of composite materials has increased over the last few decades. A crucial component of composite material is its reinforcement, which is available in the form of fibres – long and short, random/directionally oriented, and synthetic/natural (Zachariah et al., 2021). An equally crucial component of a composite is the matrix – which is usually a polymer, thermoplastic or thermosetting.
Naturally derived fibres are called natural fibres and have several advantages over generally used synthetic fibres such as E-glass, carbon, and aramid fibres. These include biodegradability, easy processing, and availability in abundance, and low cost (Qi et al., 2019; Sanjay et al., 2018). Plant-based natural fibres possess higher stiffness, biodegradability, and strength-to-weight ratio as well as noticeable mechanical properties if the fibrils within the fibre are oriented uniaxially (Petroudy, 2017). On similar lines, matrices are also accordingly used in a composite to enhance its biodegradability and reduce the processing cost (Ray and Sain, 2017).
Natural fibres possess a hydrophilic nature due to the presence of hydroxyl groups in their constituents – mainly cellulose (Li et al., 2007). Cellulose is one of the main constituents of natural fibres along with hemicellulose, lignin, pectin, waxes, and other impurities (Komuraiah et al., 2014). In addition to this, there also exist irregularities on the fibre surface that could result in stress concentration at those points resulting in lower fibre strength (Nayak et al., 2021).
To counter these shortcomings of natural fibres, surface treatments are employed. These comprise alkali treatment (Maulana et al., 2021), benzoylation treatment (Madhu et al., 2020), silane treatment (Atiqah et al., 2018), bacterial treatment (Noureddine, 2019), enzymatic treatment (George et al., 2016), sodium chloride (Setyayunita et al., 2022), etc. thereby making it more compatible with the resin.
Alkali treatments target the functional groups within the natural fibres that contribute to their hydrophilic nature. The removal of hydroxyl groups by alkali treatments, which are responsible for the hydrophilic nature, causes the fibres to become hydrophobic, eliminating the cause for weak interfacial bonding (Sahu and Gupta, 2020).
There is a lot of focus on developing wood-based products including agricultural by-products for structural applications in many of the countries in the Indian sub-continent and South East Asia (Azmi et al., 2019; Hwang and Oh, 2020; Iswanto et al., 2020; Jamaludin et al., 2020; Jose et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2021; Sumardi et al., 2022; Wibowo et al., 2021). Grewia serrulata (GS) trees are found in many locations in India, mainly the Western and Eastern Ghats and regions in the state of Assam, and belong to the Tiliaceae family. Such trees are about 12 to 15 feet tall, bush-like evergreen vegetation. The tree possesses slender branches and grey bark with visible striations (Naidu and Kumar, 2015; Nitin et al., 2018; Senthilkumar, 2010). Traditionally, such fibres are being used by the rural population in making threads, bags, mats, knots, and baskets. Experimental investigation from the past, to explore the potential of GS fibres extracted from the bast of the tree, has shown promising results. The GS fibre-reinforced composites were subject to alkali treatment with 5% NaOH (Mahesha et al., 2016). It was seen that the composites made with treated fibres could withstand 35.79% more tensile stress than untreated fibre-based polyester composites. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis revealed the failures in treated fibres to be only at their ends, which was not the case in untreated fibres. The failure at the ends of the fibres indicated that more amounts of fibres were being utilized in the load transfer, owing to the chemical treatments (Mallick, 2007). The GS fibres were also chemically treated through permanganate, silane, and acetylation treatments (Mahesha et al., 2017; Mahesha et al., 2018). An improvement of 150% was seen in the tensile modulus of silane-treated fibre-reinforced polyester composites, with a significant increase in the tensile strength of acetylated and alkali-treated fibre-reinforced polyester composites. Additionally, an increase in the flexural modulus and flexural strength was also seen in acetylated, permanganate, and silane-treated fibre-reinforced composites over untreated panels.
Chemical treatments performed on GS fibres so far only involve a fixed concentration of the reagent used. Limited information exists on the effect of chemical treatment on the mechanical properties of GS fibres when the chemical concentration is varied over a fixed duration. Therefore, in the present study, the fibres have been subjected to standalone sodium hydroxide (NaOH) treatment as well as NaOH + silane treatments at varying concentrations for a fixed duration to find out the optimum concentration for the best properties of the fibre. This research helps enhance the knowledge database of GS fibres by exploring means of improving their properties by considering NaOH and silane as chemical reagents. Chemically treated fibres can be used as reinforcements in the making of natural fibre-based composites of low to moderate-strength structural applications such as office partitions, furniture, shelves, etc.
2. MATERIALS and METHODS
For the extraction of the fibres, well-grown branches of the trees were retted in still water for four days. Beating and shaking such branches release the bundles of fibres. From these bundles, fine individual fibres were split manually, segregated, and dried under the sun for a couple of days. Such extracted fibres were stored in airtight polyethylene covers till used for further processing. Fibres extracted were cleaned with distilled water to rinse off any external particles such as dust/impurities from the fibre surface. Post rinsing, the fibres were dried in a hot air oven at a temperature of 45°C for 30 min. The fibres are flat and have a rectangular cross-section. For alkaline and alkali + silane treatment as well as tensile testing of fibres, 20 samples were studied each.
The designation of the natural fibres subjected to various chemicals is presented in Table 1. These were namely NaOH and NaOH + silane treatments. Both the chemicals were procured from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Private Limited, Bengaluru, India, and were used without any further purification.
The dried fibres were treated with 3%, 6%, and 9% (w/v) aqueous NaOH solution. The fibres were immersed in the solution for the duration of 4 h. Post the treatment; the fibres were washed with distilled water and 5% (w/v) aqueous acetic acid to neutralize any traces of the alkali on the surface. This was followed by drying in a hot air oven for 1 h 15 min at 50°C.
The 3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate was employed as silane. Completely dried fibres at room temperature were dipped in 0.2% silane solution (2 g of silane in 1,000 g solution of ethanol and distilled water in the ratio of 4:6) for 2 h. After the treatment, the solution was drained off the fibres. Then the fibres were dried in a hot air oven for 1 h 15 min at 50°C.
The density of the treated as well as untreated GS fibres was measured using a digital density meter (CAS 234 model; Contech Instrument Ltd., Navi Mumbai, India). By explaining the variation in physical parameters of the natural fibres, one can easily interpret the structural changes in the same. One such physical parameter is density (ρ) which gives the measure of the compactness of the network of fibres. Knowledge of the density of fibres helps in estimating the density of the composite made out of the treated fibres. The density meter follows Archimedes’ principle where the weight in air is measured (wa), and the weight while submerged in a liquid of known density (ρb) is measured (wb). Density is then computed by using equation (1).
The tensile strength or ultimate tensile strength of natural fibre is the maximum stress it can withstand till failure. The GS fibre specimens for tensile tests were prepared and tested as per ASTM D3822 – 01 standard. The testing was done on a Universal Testing Machine (3366 Model; Instron, Norwood, MA, USA) at a feed rate of 10 mm/min with a gauge length of 50 mm. Twenty samples were considered for tests and average values were computed.
Chemical treatment provided to the natural fibres leads to changes in their chemical constituents. These changes are responsible for variations in the size, density, and strength of the fibres. To determine the changes in the chemical constituents of the GS fibres, gravimetric analysis as proposed by Vax Soest (1963) was employed. Cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin were estimated by neutral detergent fibre (NDF), acid detergent fibre (ADF) and acid detergent lignin (ADL). NDF = Hemicellulose + Cellulose + Lignin + minerals. ADF = Cellulose + Lignin + Minerals. Hemicellulose = NDF – ADF; Cellulose = ADF – ADL; Lignin = ADL (Graupner et al., 2019; Shenoy Heckadka et al., 2022b). Fig. 1 shows the various stages in gravimetric analysis.
To investigate the changes on the surface of the GS fibres due to the chemical treatment, SEM (EVO 18 Special Edition Model; Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) was employed. The fibres cut to 10 mm in length were coated with Gold-Palladium before placing them in the vacuum chamber. The SEM was operated under variable pressure mode with an accelerating voltage of 20 kV and a working distance in the range of 8.5–10 mm.
TGA was carried out to evaluate the changes in chemical constituents including cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin wax, pectin, and moisture in addition to determining the thermal stability of the natural fibre. TGA of the GS fibres in this study (treated as well as untreated) was performed on a Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan), DTG – 60H model, in a temperature range of 25°C–500°C. A sample weight of 10 to 12 mg was considered. The samples were heated from 25°C to 500°C at a ramping rate of 10°C/min under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reduction in the weight of the fibre sample is observed concerning the increasing temperature (Saheb and Jog, 1999). These reductions in certain temperature ranges are mapped to the constituents of the natural fibre.
3. RESULTS and DISCUSSION
The variations in density values of the GS fibres subjected to various treatments are presented in Table 2. The highest density observed was 1.5812 (g/cc), in the case of TG9S, which was 26.5% higher than the density of RG. The silane treatment facilitates a more effective removal of the lighter constituents of the fibre as the silane-treated fibres exhibit enhanced density in comparison to their non-silane counterparts. This can be attributed to the siloxy bond formation with the hydroxyl group of the lignocellulosic fibre (Xie et al., 2010). With increasing concentration, a proportionate increment in the density can be seen as well. As this is a natural fibre, the structure of the natural fibre would be such that the non-cellulosic contents of the fibre such as hemicellulose, pectin, lignin, etc. would occupy a large amount of volume in the fibre. However, the mass of these constituents is not as much as cellulose. Hence, the removal of these contents causes a substantial change in the volume and a slight change in the mass of the fibre itself. This results in an increment in the density of the fibre. It is mainly the cellulosic content of the fibre that contributes to its strength. Therefore, an increment in density can be seen as an indicator of the effective removal of the non – cellulosic constituents of the fibre (Nayak et al., 2021). This is a function of silane treatment as well as the concentration of NaOH.
| Designation of natural fibers | Density (g/cc) | Standard deviation (g/cc) |
|---|---|---|
| RG | 1.2502 | 0.03 |
| TG3 | 1.3297 | 0.05 |
| TG6 | 1.3824 | 0.01 |
| TG9 | 1.4327 | 0.04 |
| TG3S | 1.4521 | 0.07 |
| TG6S | 1.5289 | 0.09 |
| TG9S | 1.5812 | 0.05 |
The tensile properties of GS fibre specimens subject to NaOH treatment and NaOH-silane treatment at various concentrations are shown in Fig. 2. With the increasing concentration of the alkali, the tensile strength is enhanced. The TG3, TG6, and TG9 had tensile strengths of 4.42%, 13.33%, and 55.14% higher than RG. This can be attributed to the removal of surface impurities and reduction of hemicellulose, and lignin content with the fibre. With the increasing concentration of the alkali, the extent of removal of these constituents increased, which resulted in improved tensile strength. The highest tensile strength obtained was 221.71 MPa in the case of TG9S, which happens to be about 120% greater than that of tamarind fruit fibres (Kini et al., 2018), and in the operational range of coir, bagasse and oil palm fibres (Gholampour and Ozbakkaloglu, 2020).
The silane-treated counterparts of TG3, TG6, and TG9, namely TG3S, TG6S, and TG9S respectively exhibited superior properties in comparison to the former. The tensile strength of TG9S, TG6S, and TG3S is 16.4%, 27.94%, and 32.45% higher than TG9, TG6, and TG3 respectively. Silane treatment of the fibres with alkali produced a deposition on the fibre surface, which filled the grooves on the lateral surface of the fibre (Bilba and Arsene, 2008; Makowski, 2020; Raharjo et al., 2018). The coating produced because of this chemical treatment allowed for a higher extent of mechanical interlocking on the fibre surface, resulting in a higher tensile strength (Kabir et al., 2012; Shenoy Heckadka et al., 2022a). Alkali treatment causes hydrolysis in the previously hydrogen-bonded molecules of hemicellulose, lignin, and cellulose; however, it is to be noticed that the extent of hydrolysis is proportional to the strength of the alkali and the duration of the treatment (Ali et al., 2015; Li et al., 2007). This further explains the increase in tensile strength of the fibres.
Proportions of chemical constituents, namely, cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin of untreated and chemically treated GS fibres are presented in Table 3. Among the treated fibres, chemical constituents of only those that gave the highest strength were determined. Cellulose content was in the range of 51% to 53%; hemicellulose in the range of 15% to 22% while lignin was estimated to be in the range of 9% to 12%. With NaOH treatment, the cellulose content dropped to 40% to 51%, hemicellulose content dropped to 10% to 14% and lignin content dropped to 7% to 8%. A combination of NaOH and silane-treated fibres showed cellulose in the range of 41% to 50%; hemicellulose in the range of 9% to 12% and lignin in the range of 5% to 7%. This explains and supports the variation in density and tensile strength of the fibres. From the results, it can be observed that the silane treatment provided proved to be more effective in reducing the hemicellulose and lignin content than just NaOH and thus explains the higher strength obtained with silane treatment over NaOH treated fibres. Similar observations were reported in the case of pineapple leaf fibres, kenaf fibres and bamboo fibres (Asim et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2020).
| Designation of natural fibers | Cellulose (%wt) | Hemicellulose (%wt) | Lignin (%wt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RG | 51–53 | 15–22 | 9–12 |
| TG9 | 40–51 | 10–14 | 7–8 |
| TG9S | 41–50 | 9–12 | 5–7 |
Fig. 3(a) is the sectional view of the RG specimen. The lateral dimension measured was approximately 1.052 mm and the vertical dimension measured was approximately 252 μm. Fig. 3(b) shows the sectional view of the final, TG9S specimen. This had approximate dimensions of 1.956 mm and 263.7 μm in horizontal and vertical directions respectively, which were 85.93% and 4.7% higher than the dimensions of the untreated fibre. This could be due to two reasons, the first being the swelling of the fibres due to the alkali treatment. This swelling occurs due to the alkali treatment causing a change in the fibre structure – changes in active spots for hydrogen bonding as well as in the cellulosic structure (Chand and Fahim, 2021). Secondly, the hemicellulose in the fibre acts as a supporting matrix for the cellulosic microfibrils, which are seen as straight lines on the fibre. This happens because hemicellulose is hydrophilic and highly susceptible to alkali treatment in terms of its solubility (Patel and Parsania, 2018). The removal of the supporting structure of the microfibrils caused them to disperse in a way that could be conceived as a substantial increase in the lateral dimension of the fibre. As can be seen in Fig. 3(a), the residual sheath present in the untreated fibre could act as a stress-raiser, i.e., becoming a region of stress concentration, resulting in lower tensile strength of the fabric. However, this is absent in the final treated TG9S specimen. This indicates the effective removal of stress-raisers by the alkali treatment (Nayak et al., 2021).
Fig. 4(a) through 4(f) show the surface morphology of the fibres when subjected to the above-listed treatments in Table 1. Like Fig. 3(a), the residual sheath can also be seen as the randomly oriented fibril in Fig. 4(a), which is the surface picture of TG3. Impurities, which are in the form of randomly oriented clusters, between adjacent microfibrils are also visible. These irregularities alongside the residual sheath contribute to the low strength of the untreated fibre. However, in comparison to RG, TG3 does exhibit some level of orientation of the cellulose microfibrils, labelled in Fig. 3(b).

The extent of this alignment and prominence of microfibrils increases with the increasing concentration of the alkali. This removes the surface impurities as well as irregularities. As stated in the tensile strength of these specimens, the ones treated with silane exhibit superior properties in comparison to their alkali-only counterparts. When TG6 and TG6S are compared, TG6S, in addition to the enhanced visibility of the cellulose microfibrils, also exhibits a crosslinked network. This can be attributed to the bonds formed by the silane with the active sites triggered by the alkali treatment. These crosslinked networks act as a mechanical interlock and result in enhanced mechanical properties of the fibre as seen before (Kabir et al., 2012; Shenoy Heckadka et al., 2022a). These crosslinks are absent in case of the specimens such as TG3, TG6, and TG9, which are solely treated with the alkali.
Additionally, the alkaline treatment of the fibres produces a deposit, which results in a smooth fibre surface as seen in Fig. 4(e) (Shenoy Heckadka et al., 2022a). As discussed before, since the hemicellulose, which acts as a bonding element for the cellulose microfibrils is removed by the alkali treatment, the cellulosic microfibrils are bound to either disrupt the network or get loose. This can be seen as labelled in Fig. 4(f).
Fig. 5 and Fig. 6 show TGA comparisons of treated and untreated GS fibres. In both the figures, in the first stage of thermal degradation (50°C–100°C), similar trends are observed – indicating loss of moisture through vapourization. The second stage of degradation starts at 200°C. This indicates the decomposition of hemicellulose and pectin to 350°C. In the case of TG3, TG6, and TG9, these curves are overlapping. This indicates equal effectiveness of the removal of hemicellulose and pectin from the treated fibres (Asim et al., 2020).
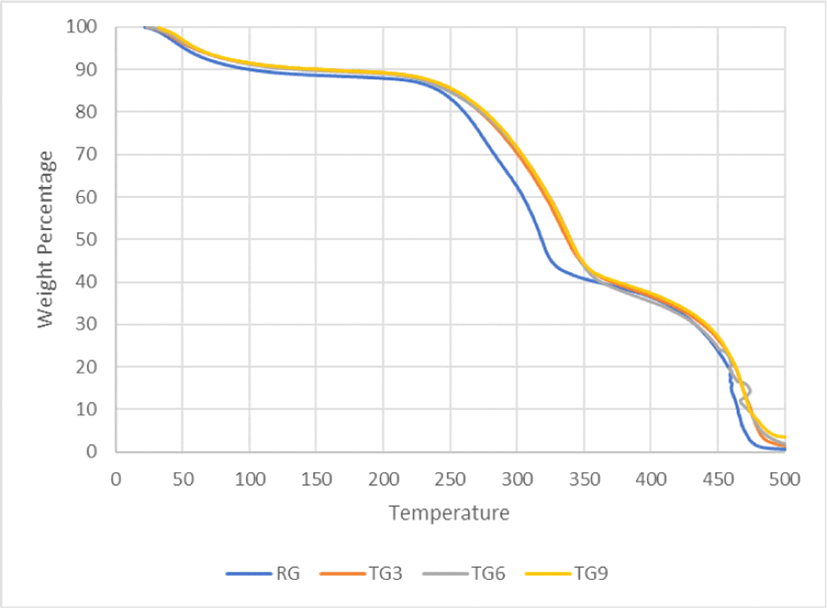
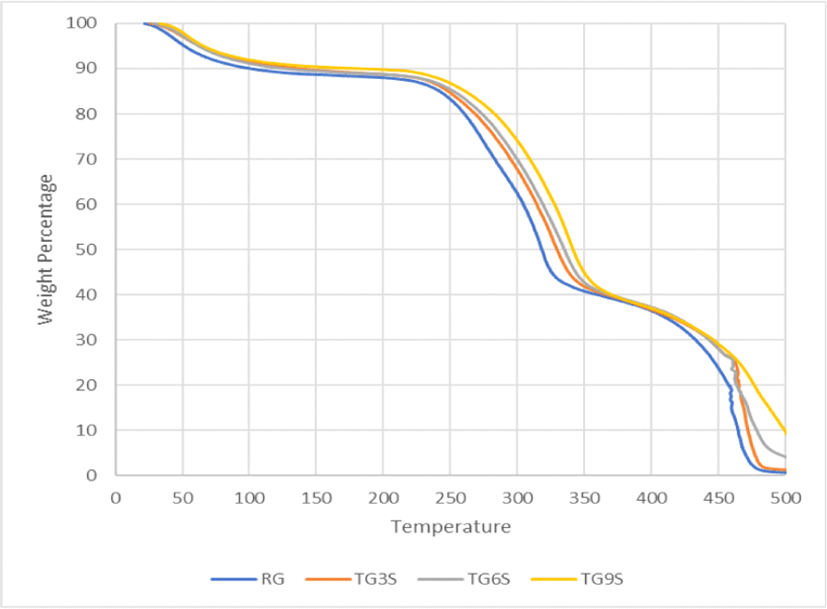
On the contrary, TG3S, TG6S, and TG9S follow distinct curves in the region of 200°C–350°C. This implies that the extent of removal of hemicellulose from the fibre is a function of the silane treatment and NaOH concentration, as here, with the increasing concentration of NaOH followed by a fixed concentration of silane, the amount of degradation of the fibre in this region reduces – indicating absence or reduction in the amount of hemicellulose. This is followed by the third stage of degradation onwards from 350°C–500°C which comprises of degradation of cellulose and lignin in the fibre (Asim et al., 2020). Here again, the curves overlap for a major range of the temperature. As explained earlier, alkali treatment causes hydrolysis in the hydrogen-bonded molecules of hemicellulose, lignin, and cellulose, but to get significant changes in the TGA profile, a larger extent of hydrolysis is necessary which was not seen in this case, as the amount of alkali concentration variations was 3%, 6%, and 9% which is not that significant and thus explains the overlapping nature of the TGA curves. A larger variation of alkali concentration in the range of about 10% to 30% generally shows changes in TGA graphs (Akram Khan et al., 2011; Li et al., 2007; Sahu and Gupta, 2020).
4. CONCLUSIONS
Upon chemical treatment with NaOH, it was observed that the density and mechanical properties increased with the increasing concentration of NaOH. The highest density was seen in the case of TG9S, which was 97.832% higher than RG. This was mapped to the effectiveness of the removal of lighter, mechanically inactive substances such as hemicellulose from the fibre. An improvement in the tensile strength of the fibres was observed with the increasing concentration of NaOH. Similar trends were observed in the case of NaOH + silane treated fibres, which were in fact, superior to their alkali-only counterparts. This was attributed to the mechanically interlocking siloxy bonds formed with the active sites of cellulose, which were in turn formed after alkali treatment. These findings were further validated with the visible crosslinks forming on the fibre surface as seen in the SEM images. Likewise, the removal of hemicellulose was also proved by observing the weight loss in the second stage of TGA apart from estimating the chemical constituents. The weight loss obtained in the 200°C–350°C region in thermogravimetry graphs confirmed the removal of hemicellulose, which validated the inferences regarding improvement in tensile strength of the fibres due to the removal of hemicellulose. Hence, the obtained density and the highest tensile strength with NaOH and silane treatment of the fibres makes them suitable for light load applications – such as car seats, door handles, rail berths, etc. and makes way for a green composite if employed with appropriate natural resin.










